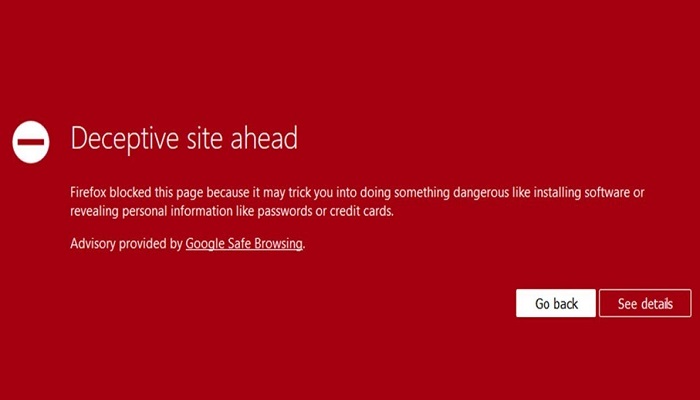
Deceptive Site Ahead has become common in recent days, you may think this is a problem, but the truth is that your web browser is only trying to protect you from deceptive and dangerous websites.
Let’s start by understanding the meaning of deceptive. According to dictionary.com something being “Deceptive means intended to or tending to deceive—to lie, mislead, or otherwise hide or distort the truth.”
Now you can see why I said that your browser is protecting and notifying users of the site a possible treat ahead if they log in to the site.
“Everything was working fine last night, then this morning Google started showing an ugly Deceptive site ahead warning, its a red page warning on my website. I normally have about 700 visitors each day, it is already 10:30 pm and I have gotten only 37 visitors. Please help me, if this continues my site will be useless.” This was the message I received from a fan.
While this problem can be alarming, the good news is that the deceptive site ahead can be fixed very easily.
Continue reading to see how to solve deceptive site ahead permanently.
What does ‘Deceptive Site Ahead’ mean?
The deceptive site ahead warning message is actually rendered by Google as a notification to the visitors about the possible compromised state of a particular website.
If your website has this warning, then it is possible that hackers may have compromised your website and be using it for malicious purposes like Phishing where they show fake pages to the site visitors in other to acquire their credentials.
Why is your website showing deceptive site ahead?
Phishing and malware are the major reasons why Google sees a website as deceptive or fake. But, there are lots of other reasons that can make the deceptive site warning trigger on your website, I will explain them all here.
1. Phishing
Phishing is a type of cybercrime that involves fraudulent attempts to deceive individuals or organizations into providing sensitive information, such as login credentials, financial details, or personal data.
The attackers, known as “phishers,” often masquerade as legitimate entities, such as banks, social media platforms, or online services, to trick their targets.
Phishing attacks are typically carried out through various channels, including:
- Email Phishing: Phishers send deceptive emails that appear to be from a trustworthy source, urging recipients to click on malicious links or provide sensitive information.
- Spear Phishing: Similar to email phishing, but more targeted. Attackers tailor their messages to specific individuals or groups, making them more convincing.
- Smishing: Phishing attacks conducted through SMS or text messages.
- Vishing: Phishing attacks that use phone calls, where the attackers pretend to be someone else to extract sensitive information.
- Pharming: Involves redirecting users to fraudulent websites, even if they enter the correct URL in their browsers.
2. Malware
Malware is a broad term encompassing different types of malicious software that aim to exploit vulnerabilities in computer systems.
These programs are created by cybercriminals to gain unauthorized access to websites, compromise user data, and disrupt website functionality.
Understanding the various types of malware is crucial in developing effective defense strategies.
Malware is also one of the reasons Google may flag a website as ‘Deceptive Site Ahead’.
Malware can be inserted into a website in several ways, these are called cyber attacks.
How Malware can be inserted into a website
- Vulnerabilities in Software: Outdated or poorly configured software can create entry points for cyber attackers to inject malware into a website.
- Phishing Attacks: Phishing emails or messages can trick website administrators into revealing login credentials, which cybercriminals then use to access and infect the site.
- File Uploads: Malware can be uploaded to a website through insecure file upload mechanisms, allowing attackers to execute malicious code.
- Malicious Code Injection: Cyber attackers can exploit vulnerabilities in a website’s code to inject malicious scripts that infect visitors’ devices.
3. Not Having a Proper SSL Certificate
Google has made SSL mandatory for all websites when it included it as one of its SEO ranking factors, especially for sites where users have to provide some valid information.
Once a site has its Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) certificate properly installed, a padlock sign will appear on the URL bar when the site is visited. And the protocol then becomes HTTPS (meaning, Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure), on like the default HTTP.
The difference between HTTP and HTTPS is the “S” which stands for secure. Now, you can see that the unsecured protocol is not secured. This can be a reason Google can consider a website to be deceptive.
We believe Google is strict with its policies on sites where users have to provide their credentials. Any website that has a user login should have an SSL certificate.
We have seen cases of sites flagged as “deceptive” reason because they are yet to move from HTTP to HTTPS.
Installing an SSL certificate on your site is not enough, after installing the certificate it is advisable to force redirect it from HTTP to HTTPS. So whoever tries to visit the site via the insecure protocol will be forcibly moved to the secured protocol.
Having some of your web pages or your site visitors accessing your site as HTTP and some as HTTPS will give Google a mixed signal. This mismatch can be a reason why your website may be flagged as deceptive by Google.
Again, you should make sure your site renews its SSL certificate before it expires. If you don’t know how to purchase the SSL certificate, simply contact your web hosting company to guide you. Each hosting may have a different way by which SSL is being installed on their server.
4. Faking Domain Name
Faking a domain is responsible for so many websites becoming deceptive. You may be asking how is it possible to fake a domain name. I will break that down here.
There are so many domains on the internet that is very similar to an existing domain, this means that site visitors may visit the wrong website without even knowing. Once Google notices this they will immediately flag it as deceptive.
Let me give you an example.
It will be very difficult for web users to differentiate between
- firstbank.com and fistbank.com (changing the domain like the second one to look similar to a verified domain name is deceptive)
- fedex.com and fedex.co (both are different but the second can deceive web users, it is also deceptive)
- remita.net and remitar.net or remitta.net or remita.org (All are different, only the first is the original site)
Seeing both examples above the domains will easily be tagged as deceptive by Google, not because the domain name is not valid, but because web users can actually mistake one for another. So many fraudsters have used this medium to steal from people. They can claim to be a particular bank, just for users to visit and provide their login details.
Therefore, if your site is deceptive, it will be advisable you conduct research to know if there is a verified site that shares almost the same domain name as yours.
If yes, and your website is legitimate, then you may have to write to Google or contact your hosting to guide you on what to do next. But before doing this, you may need to register your website as a company so it will have legal backing.
5. You offer suspicious downloads on your site
As a site owner, whatever you allow your users to download matters a lot. If you are providing dangerous downloads your site is at the risk of getting flagged. A suspicious download can be any of the following,
- Cracked Software
- Files infected with a virus
- Free download of premium files
- Downloads that have copyright issues.
How Does “Deceptive Site Ahead” Impact Your Site?
As mentioned earlier seeing a deceptive site ahead warning appearing on your site indicates that it has been possibly hacked. If you are the site owner, you will be at risk of having all the data on your site stolen or deleted.
If malicious code causes damage to your site, you will have to spend a lot to get the problem fixed.
Hiring a Web developer to recover the site may cost over $500 depending on the nature of the problem.
In the worst scenario, you are likely to face legal consequences for failing to protect your visitors’ information.
If the issue goes a long way, it may destroy the brand and the brand’s reputation. This will cost the brand its customers trust.
For sites running as eCommerce, it will impact negatively the company’s conversion and sales rates.
Another negative effect is that the site traffic will also suffer hugely as Google will actively hinder visitors from easy access to the site.
Even if you restore the hacked site back, you will still lose a lot of search engine optimization.
If your malware infested site stays for a very long period of time, your hosting may decide to take down the site or suspend the hosting.
How to ignore and visit a Deceptive site Ahead website
Once a site has the deceptive site ahead warning, as we said earlier it’s a browser response, echoed by Google Safe Browsing.
This error or notification does not totally prevent the site user from accessing the site. It only gives the user prior notice, nevertheless, the user can still choose to access the site if they so, please.
We will be looking at how to access deceptive sites on Google Chrome browser and Mozilla Firefox.
How to access deceptive sites on Google Chrome Browser
After entering a deceptive URL on the Chrome browser, click on details to view the dropdown and click “visit this unsafe site” as shown in the image above.
How to access deceptive sites on Mozilla Firefox Browser
The Firefox deceptive page is very similar to that of Chrome. Simply click on details, to view to dropdown, then click on “ignore the risk”.
How to stay safe while visiting a deceptive website
Above we have shown how to access a deceptive website by ignoring the risk. While doing this you are exposing yourself to threats.
The best way to stay safe after doing this is by refusing to provide any valid information. If the site requires you to login, do not provide your username or password.
If you are requested to register, just know that any information you provide during that registration may be manipulated or stolen.
If you have to register then never provide valid information, for such a purpose. If your email address is requested, you can create an email that you can abandon for the purpose.
How to Fix Deceptive Site Ahead on any Website
The deceptive site ahead warning that shows when trying to access some websites means that there is a very high tendency that attackers have compromised your website and are possibly using it for phishing purposes.
This means that the site visitors are being served fake web pages that are tricking them into revealing their personal credentials, credit card details, and other vital information. Which attackers will receive on their shady servers.
First Step: Find the Cause of Infection
The first and most crucial step while fixing the deceptive site ahead issue is to identify the infection/problem. The problem could be present only on a single web page, folder, file, or even the entire hosted website.
To identify the actual issue, you have to take a number of steps as explained below:
1. Doing the Manual Search
While the manual search may not be an ideal way for malware detection considering that it requires prior knowledge and expertise to spot the malware, it can be a great start if you know a lot about your website.
These are the steps;
- First, visit the site from another device and ignore the deceptive warning.
- View the source of your website, you can do this by right-clicking outside any element and selecting the View page source option. This will open the source code of your web page in a new browser tab.
- Then you can look for suspicious third-party javascript files, HTML tags, iFrames, or any fishy-looking element that is loading on that page.
- Open the affected file manager of your web server and view the source code of those files that are housing the malicious code.
During the manual search of the cause, there are some resources that you have to check for fixing deceptive site ahead warning issues;
- Unknown admin(s) in the dashboard.
- All plugins and themes that were recently installed.
- New login in the database.
- Files with strange names or base64 encoded characters.
To check the recently modified files on your server, let’s say eg for the last 30 days, log into your server via SSH and run the command below:
find . -type f -mtime 30
You can change the value from 30 to the number of days of your choice. A word of caution, there are some files that are automatically modified by the server, so make sure to verify carefully for malware in such files before removing them.
2. Using Malware Scanners
There are lots of free online tools and malware scanner plugins available that can be used to find the infected web pages on your website all at once.
This is the quickest approach to detect all infected pages and files on a website. Astra Security’s malware scanner is among the best in the market.
It helps detect the slightest changes in your files. It even lets you review your files in its View File Difference interface.
These malware scanners can detect malware by scanning your publicly available files’ source code. These scanner results are somehow limited when compared to the paid ones. However, it can still help you identify if your site is hacked or not.
Simply enter your website URL in the widget and scan your website for over 135 security tests. It can even help to detect Google blacklisting aside from detecting your pages that are infected with malware, SEO spam, and so on.
3. Using Google Search Console

Google Search Console is an amazing assistance for locating infected pages on your website.
In the “Security Issues” part of the Google Search Console, Google will list the security issues that are present on your website.
First, you need to confirm ownership of your website. This actually means that you have to prove to Google that you own the site. This can be done in several ways Google provided i.e. HTML tags, meta tags, etc.
Note that in a hack case, there is a possibility that attackers have already seized your search console as well. So for you to remove such unauthorized users, you will have to visit the property owner management page, which you will find in your Google search console dashboard.
Finally, make sure you have created a backup of your whole website before proceeding with the cleanup. Your backup is your only remedy incase if something goes wrong.
Second Step: Clean Up the Website
Now I believe you must have identified the infected files, the next step is to fix the deceptive site ahead warning are:
- First, you will have to delete all the malicious code in infected files. If you are not sure of what each code does, you may need to contact an expert for assistance.
- For all code using base64 encoding, you will have to decode it to see what it does. To decode base64 the is an online resource to decode it.
- Remove all suspicious users on the database and the dashboard and make sure you change the password of each one of them to a secure and random string.
- Delete completely all buggy or null themes, plugins, etc. Also, make sure you delete their files too.
- If any suspicious user is found on the property owner management page of your Google Console Dashboard, remove them immediately. you also have to delete all meta tags that were used for the verification of the ownership by unauthorized users.
- Alert all the users of your site to reset their credentials. Or better still you can write a code to force the users to update their password. If you don’t want your users to feel threatened, tell them that the reason is to better security.
- Finally, add a compulsory Two Fator Authentication (2fa) on your site and server.
Third Step: Submit your Site for Review
This is the last step to fix the deceptive site ahead warning alert. All you have to do is to submit the site to Google Console for a review. Before doing this, ensure you have double-checked your website for malware and backdoors.
If all is taken care of, then submit the site for a review using the following steps:
- Login to Google Search Console with your Google account.
- Click on the Security Issues report section and select “I have fixed these issues”.
- Thereafter, click on the Request a review.
- Explain in detail the steps you took in fixing the warning alert.
- Finally, click Submit Request as shown in the image above. If there was a case of multiple issues, repeat the process for each.
- After this, wait as this can take between 24 hours to 72 hours for Google to review your request.
If everything is fine with your site, Google will remove the blacklisting and de-indexation of your web pages.
Note that it can take some days for your web pages to get re-indexed to regain their rankings entirely.
Fixing a deceptive site ahead of warning issues can prove to be very difficult at times depending on the type of infection.
The best thing to do is to protect your site against such kind of situation taking take proactive steps to secure your website properly.
You make use of a firewall, secure developments, and other maintenance practices, this will do wonders for your website’s security.
How to Prevent the “Deceptive Site Ahead” Warning?
- Invest in Security Plugins and Software: This will help prevent threats on your site and help you detect any possible threats on time.
- Do Regular Updates on your website: Don’t just build a site and abandon it. Make sure you run updates at least every 4 months.
- Always practice Safe Browsing: This will help your browsing against bad sites and protect your computer against threats.
- Protect all logins on your site: You can make use of Two Factor Authenticator (2FA) and Recaptcha.
- Manage your user Activity: The mindful of the roles users can play on your site, and let there always be moderation.
- Use a valid SSL Certificate on your site: Always make sure that your site has a valid SSL, and renew the SSL before it expires. This also helps the SEO of your website.
- Choose a good and secure hosting provider: Don’t just pick and company to host your site, go with a hosting that has good reviews and track records.
RELATED ARTICLES